Understanding Biomimicry
Biomimicry, also known as biomimetics, is the practice of studying and imitating natural systems, processes, and elements to solve human challenges. Nature's designs have evolved over millions of years, resulting in highly efficient and effective solutions. Biomimicry harnesses this natural wisdom, applying it to fields such as engineering, architecture, and material science. By understanding how nature addresses specific problems, innovators can develop new technologies that are both sustainable and efficient.
The Fascinating World of Natural Inspiration
From the structural design of a spider's web to the efficient flight patterns of birds, nature offers a wealth of inspiration for technological advancement. For instance, the study of the lotus flower led to the creation of self-cleaning surfaces, as its leaves possess unique properties that repel dirt and water. Similarly, the aerodynamic design of a kingfisher's beak inspired the development of high-speed trains that are both quieter and more energy-efficient. By observing and emulating these natural phenomena, scientists and engineers are able to create innovative solutions that address modern challenges.
Revolutionary Technologies Inspired by Nature
One of the most notable examples of biomimicry in technology is the development of Velcro. Inspired by the way burrs cling to animal fur, Swiss engineer Georges de Mestral created this versatile fastening system that has become a staple in various industries. Another example is the creation of energy-efficient building materials inspired by the structure of termite mounds. Termites build their mounds with intricate ventilation systems that maintain a stable internal temperature. This natural design has influenced the development of sustainable building materials that regulate temperature and reduce energy consumption.
Biomimicry in Medicine and Healthcare
Biomimicry is also making significant strides in the field of healthcare. Researchers have drawn inspiration from the adhesive properties of gecko feet to develop medical adhesives that can be used in surgical procedures. These adhesives mimic the gecko's ability to stick to surfaces without the need for traditional glue or sutures. Additionally, the study of shark skin has led to the development of antibacterial coatings that help reduce the spread of infections in medical settings.
The Future of Biomimicry
As technology continues to evolve, the potential for biomimicry to drive innovation is vast. Researchers and engineers are constantly discovering new ways to apply nature's principles to solve contemporary problems. From enhancing energy efficiency to improving healthcare outcomes, biomimicry holds promise for creating sustainable and effective solutions. The future of biomimicry will likely see even more groundbreaking technologies inspired by the natural world, further bridging the gap between nature and human innovation.
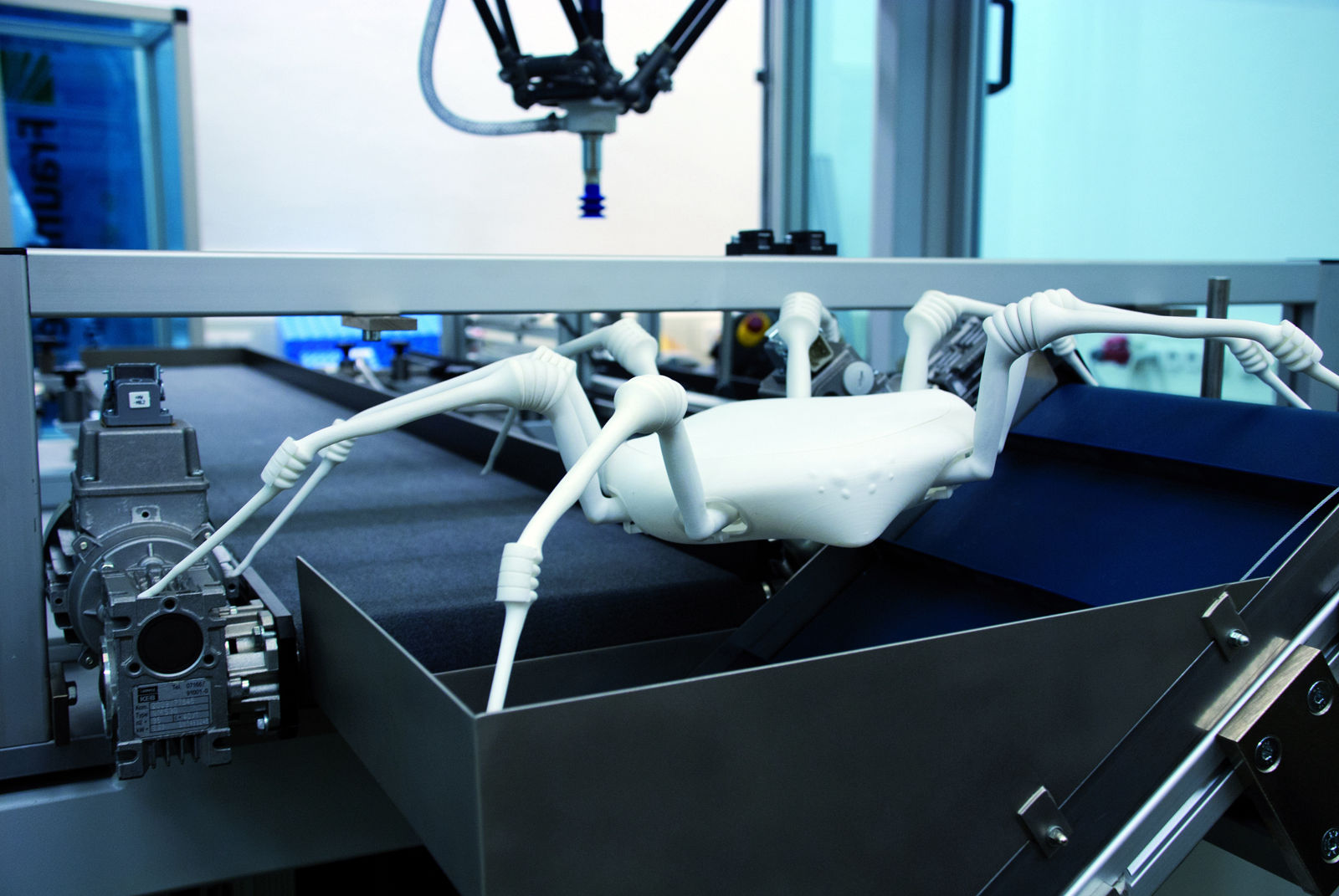
Biomimicry in Robotics and Mobility
Biomimicry is playing an increasingly important role in the field of robotics, especially in developing more agile and adaptive machines. Engineers have looked to animals such as cheetahs, octopuses, and insects to design robots that can move efficiently in challenging environments. For instance, soft robotics—a branch inspired by the flexibility of octopus arms—is revolutionizing how robots grip, navigate, and interact with delicate objects. In aerial robotics, drones modeled after dragonflies and hummingbirds achieve greater stability and maneuverability, opening new possibilities for search-and-rescue operations and environmental monitoring.
Marine-Inspired Engineering
The ocean is a treasure trove of biological innovation, and many marine organisms have inspired technological breakthroughs. The structure of whale fins has led to more efficient wind turbine blades, while the streamlined body of sharks has influenced designs for faster, more efficient swimsuits and watercraft hulls. Engineers have even mimicked the way fish swim to create undulating underwater drones that can inspect pipelines or study marine life without disturbing the ecosystem. These inventions highlight how underwater biomimicry can lead to sustainable and performance-optimized designs.
Biomimicry in Sustainable Design
Biomimicry is also reshaping how we approach sustainability in architecture and urban planning. Buildings inspired by the natural cooling mechanisms of plants and animals are being constructed to require less energy for heating and cooling. The Eastgate Centre in Zimbabwe, for example, uses a ventilation system modeled after termite mounds to regulate temperature without air conditioning. Urban planners are exploring nature-based solutions, such as green roofs that mimic forest canopies and absorb rainwater while reducing urban heat. These designs reduce ecological impact while creating more livable, resilient cities.
Educational and Ethical Dimensions of Biomimicry
Beyond its technological applications, biomimicry is influencing how we educate future innovators and approach ethics in design. Many educational institutions are incorporating biomimicry into STEM curricula to promote systems thinking, creativity, and environmental awareness. Ethically, biomimicry encourages designers to view nature not merely as a resource to exploit, but as a model and mentor. This shift in perspective fosters more responsible innovation—where sustainability, regeneration, and ecological harmony are guiding principles rather than afterthoughts.
InventHelp: Guiding Innovators on Their Journey
Bringing an invention to life involves navigating a complex landscape of development, protection, and commercialization. InventHelp offers a comprehensive suite of services to support inventors throughout this journey. From evaluating ideas and referring resources to developing prototypes and strategizing marketing efforts, InventHelp is dedicated to helping inventors turn their visions into reality. Their expertise and support provide valuable guidance, helping inventors overcome obstacles and achieve success in the competitive world of innovation.